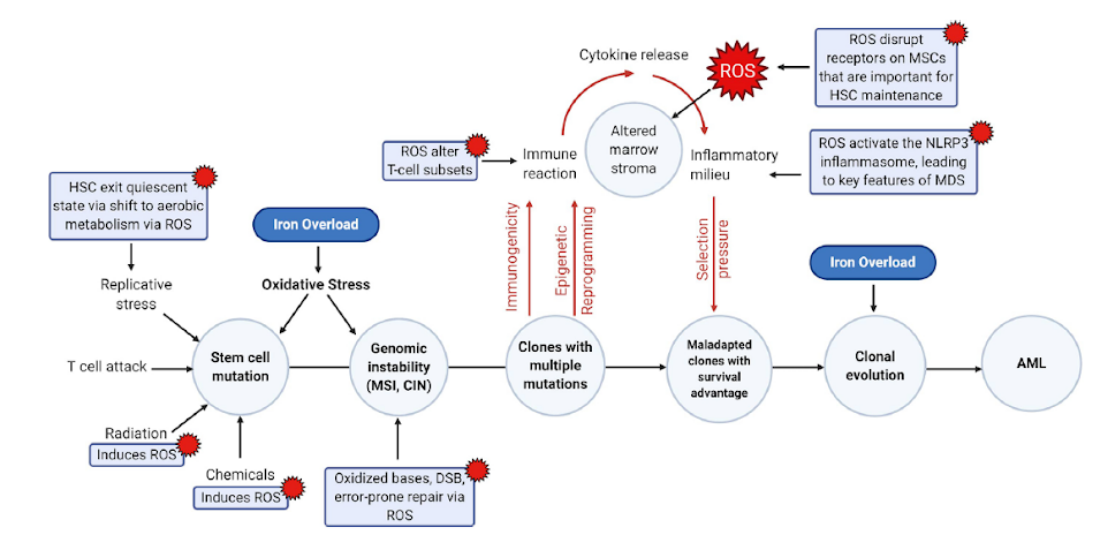
Does iron induced oxidative stress play a role in MDS pathogenesis? ROS cause HSC to exit the quiescent state via
inhibition of glycolytic enzymes, switching cells to aerobic metabolism and leading to replicative stress. ROS from
sources including iron oxidize nuclear bases, leading to DSB and error prone repair via NHEJ, resulting in further
mutations. MSC cell surface receptors important for HSC interaction are altered by ROS, leading to stromal cell
reprogramming, altering support for survival and proliferation of MDS cells. An inflammatory milieu from cytokine
release, ROS activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and alteration in immune cell subsets exacerbate impairment of
myelopoiesis and leads to selection pressure, the emergence of clones with a survival advantage, clonal evolution, and
AML progression. ICT or antioxidants may ameliorate these effects.
AML, acute myeloid leukemia; CIN, chromosomal instability; DSB, double strand breaks; HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; ICT,
iron chelation therapy; MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome; MSC, mesenchymal stem cells; MSI, microsatellite instability,
NHEJ, non-homologous end joining; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
Leitch HA & Gattermann N. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2019;141:54-72; Kim CH & Leitch HA. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2021;163,
with permission.