LPI in Lower-Risk MDS
EUMDS Registry, n=247
- Impact of LPI on survival stratified by transfusion status as a time dependent variable (censored at time of starting chelation)
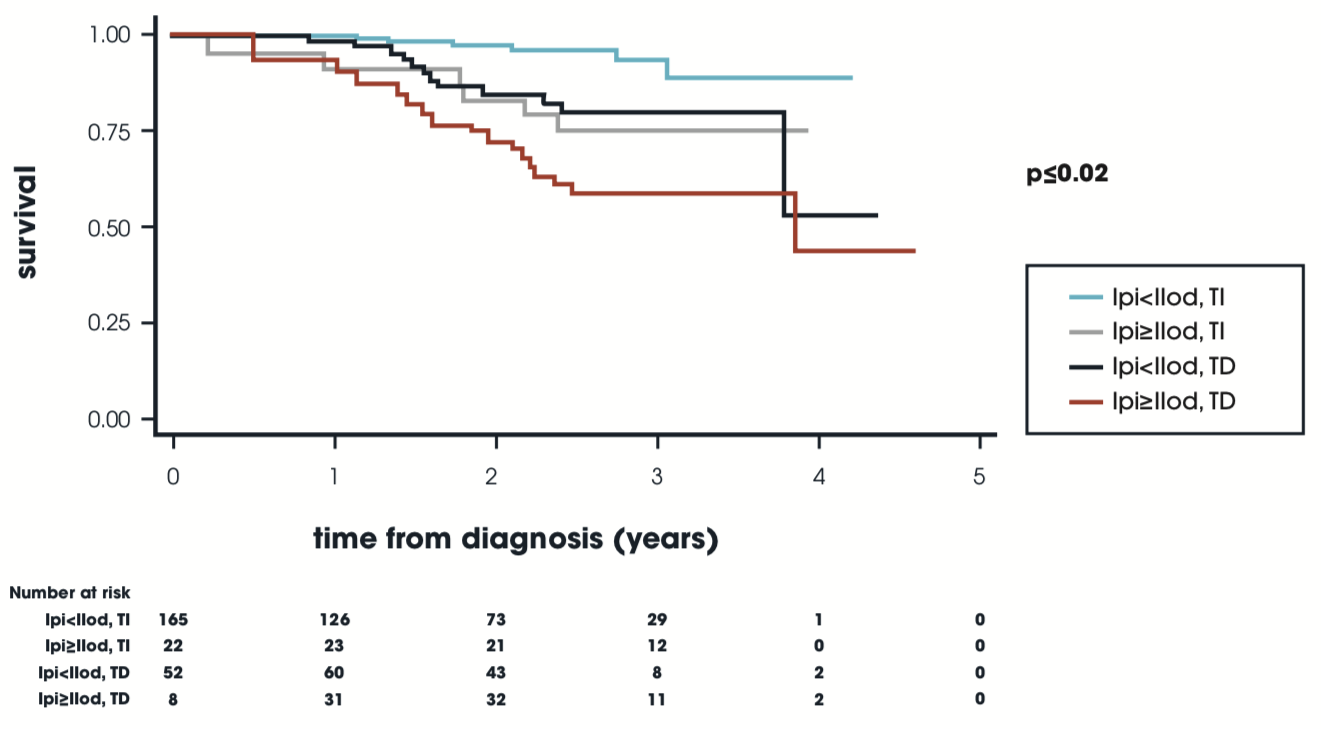
- Compared to those with undetectable LPI & TI, OS was significantly decreased in all groups, including TI with detectable LPI, after adjustment for: age at diagnosis, baseline IPSS-R, & ESA treatment (p≤0.02).
- The adjusted HR for death with detectable LPI & TD was 6.50 (95% CI 2.39-17.0).
- Conclusion: This study identifies LPI as a clinically relevant assay for detection of the toxic fraction of iron and its negative impact on HRQoL & OS in lower-risk MDS patients.